Consider a fully adiabatic piston-cylinder arrangement as shown in the figure. The piston is massless and cross-sectional area of the cylinder is $A$. The fluid inside the cylinder is air (considered as a perfect gas), with $\gamma$ being the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to the specific heat at constant volume for air. The piston is initially located at a position $L_1$. The initial pressure of the air inside the cylinder is $P_1 \gg P_0$, where $P_0$ is the atmospheric pressure. The stop $S_I$ is instantaneously removed and the piston moves to the position $L_2$, where the equilibrium pressure of air inside the cylinder is $P_2 \gg P_0$.
What is the work done by the piston on the atmosphere during this process?
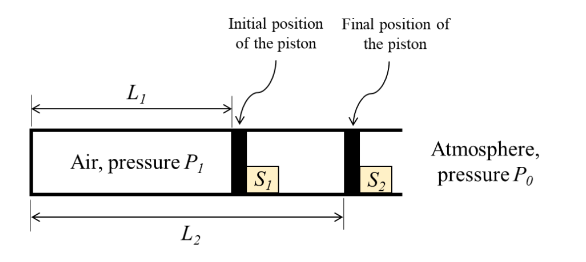
- $0$
- $P_0 A\left(L_2-L_1\right)$
- $P_1 A L_1 \ln \frac{L_1}{L_2}$
- $\frac{\left(P_2 L_2-P_1 L_1\right) A}{(1-\gamma)}$