An air-conditioning system provides a continuous flow of air to a room using an intake duct and an exit duct, as shown in the figure. To maintain the quality of the indoor air, the intake duct supplies a mixture of fresh air with a cold air stream. The two streams are mixed in an insulated mixing chamber located upstream of the intake duct. Cold air enters the mixing chamber at $5^{\circ}C$, $\text{105 kPa}$ with a volume flow rate of $1.25\text{ m}^{3}/s$ during steady state operation. Fresh air enters the mixing chamber at $34^{\circ}C$ and $\text{105 kPa}$. The mass flow rate of the fresh air is $1.6$ times of the cold air stream. Air leaves the room through the exit duct at $24^{\circ}C$.
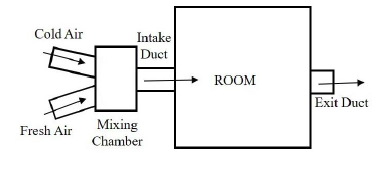
Assuming the air behaves as an ideal gas with $c_{p}=1.005$ $\text{kJ/kg.K}$ and $R=0.287$ $\text{kJ/kg.K}$, the rate of heat gain by the air from the room is _________________ $\text{kW}(\textit{round off to two decimal places}$).